Blockchain technology in banking is a revolution in enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency.
Blockchain technology in Banking is revolutionizing finance sector for a Secure future. Blockchain technology, often referred to as distributed ledger technology (DLT), is reshaping the banking industry by introducing innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. This technology, characterized by its decentralized nature and use of cryptography, is ushering in a new era of security, transparency, and efficiency in banking.

What is blockchain?
A blockchain is essentially a shared database distributed across a network of interconnected computers. Once a record has been appended to the blockchain, it becomes highly resistant to any form of alteration. To maintain uniformity across all copies of the database, the network conducts continuous verification processes. While blockchain technology initially gained prominence as the foundation for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, it is now finding a growing array of applications across various domains.


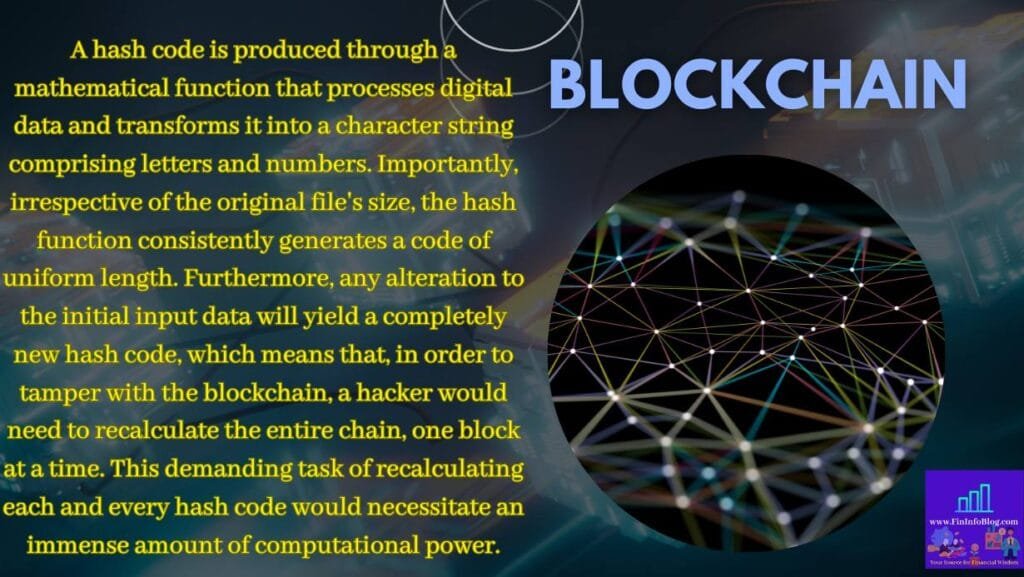
Now, the network checks the record using its algorithm to verify its validity. Upon confirming its validity, the network accepts it, and a group of such records forms a block. Each block contains a unique code called a hash, and it also includes the hash of the previous block in the chain.

A hash code is produced through a mathematical function that processes digital data and transforms it into a character string comprising letters and numbers. Importantly, irrespective of the original file’s size, the hash function consistently generates a code of uniform length. Furthermore, any alteration to the initial input data will yield a completely new hash code, which means that, in order to tamper with the blockchain, a hacker would need to recalculate the entire chain, one block at a time. This demanding task of recalculating each and every hash code would necessitate an immense amount of computational power.
A blockchain is essentially a shared database distributed across a network of interconnected computers. Once a record has been appended to the blockchain, it becomes highly resistant to any form of alteration. To maintain uniformity across all copies of the database, the network conducts continuous verification processes. While blockchain technology initially gained prominence as the foundation for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, it is now finding a growing array of applications across various domains.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Banking:
1. Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a spectrum of decentralization, which reduces the risk of a single point of failure, making it more secure. In banking, it leans towards partial decentralization to maintain a balance between security and privacy.
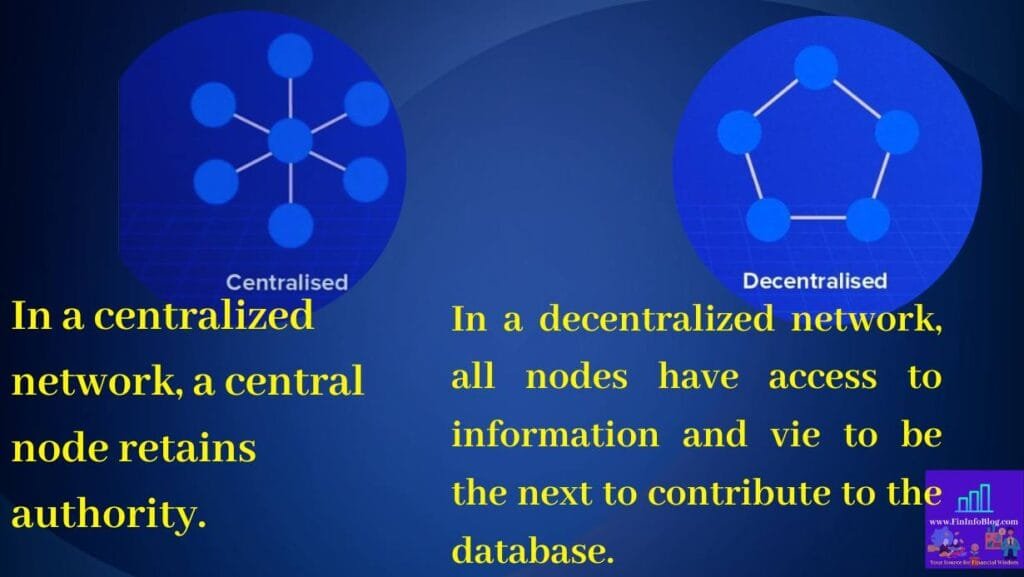
2. Transparency: Blockchain offers high transparency through open ledgers where all transactions are visible to network participants. However, in sensitive banking scenarios, some degree of privacy is preferred.
3. Security: Utilizing cryptography, blockchain ensures data protection, making it extremely challenging to tamper with or falsify records. This enhances the security of transactions.
4. Efficiency: Automation and streamlining of processes through blockchain technology lead to faster and more cost-effective transactions. Smart contracts, self-executing programs, have further improved efficiency.
5. Traceability: Blockchain allows tracking of assets and transactions from start to finish, reducing fraud and enhancing accountability.
6. Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete, creating a permanent record of all transactions.
7. Interoperability: Blockchain connects different systems and networks, facilitating seamless communication and data sharing among organizations and systems.
8. Innovation: Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, leaving room for continuous innovation and new applications in the banking sector.
Applications of Blockchain Technology in Banking:

1. International Payments: Blockchain simplifies and expedites international payments, reducing fees and intermediaries. This is especially beneficial for cross-border transactions.
2. Identity Verification: Blockchain-based identity verification systems offer secure and tamper-proof methods of verifying customer identities, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft.
Blockchain Technology Beyond Banking:
Blockchain technology extends its influence beyond the banking sector:
1. Supply Chain Management: It enhances supply chain transparency, reduces inefficiencies, and prevents fraud by tracking goods throughout the supply chain.
2. Healthcare: Blockchain secures the transfer of patient records and strengthens data protection in the healthcare industry.
3. Real Estate: It facilitates secure and transparent real estate transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries.
4. Energy Trading: Blockchain enables secure peer-to-peer energy trading, monitoring transactions and assets efficiently.
The Future of Blockchain Technology in Banking:
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize banking by increasing security, efficiency, and cost savings. Despite challenges such as regulatory issues and interoperability, banks are actively exploring and investing in blockchain. For instance, DBS has established blockchain-based businesses like DBS Digital Exchange (DDEx) and Partior, an open industry platform for real-time payments.
As blockchain technology evolves, it will find more applications in financial institutions, ensuring that banking remains relevant in a rapidly changing digital landscape. Blockchain’s transformative potential is likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance, bringing about greater security, efficiency, and transparency in the banking sector.
Blockchain may have given birth to decentralized finance (DeFi), seemingly at odds with traditional banking. DeFi relies on smart contracts for peer-to-peer transactions and operates independently of regulations. However, the future is nuanced. Most governments are unlikely to let go of the control over monetary policy and economic management. Blockchain’s potential lies in working within regulatory bounds to improve settlement, trade finance, mortgages, and the back office. Banks still have a significant role to play in this utopian future, ensuring the stability and trustworthiness of financial systems.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is on the brink of transforming the banking industry. Its promise of security, transparency, and efficiency has already begun to change the way banks operate. With continued innovation and adaptation, blockchain is set to revolutionize banking, providing benefits to financial institutions and customers alike.

How Blockchain Technology Revolutionizes the Banking Industry: Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the banking industry by enhancing security, increasing transparency, and improving efficiency in financial transactions.
Benefits of Blockchain in Enhancing Security in Banking: Blockchain enhances security in banking by using cryptography to protect data, making it extremely difficult to tamper with or falsify records. It also reduces the reliance on a single point of failure.
Blockchain’s Role in Introducing Transparency in Financial Services:
Blockchain technology introduces transparency in financial services by making all transactions visible to network participants, especially in fully public blockchains. However, it can adapt to maintain privacy when necessary.
Efficiency Gains with Blockchain Technology in Banking Processes:
Blockchain technology offers efficiency gains in banking by automating and streamlining processes. For example, it enables smart contracts, which self-execute predefined conditions, reducing the time and costs of traditional transactions.
Applications of Blockchain Beyond Banking: Blockchain technology extends its applications beyond banking into industries such as real estate transactions and supply chain management. It enhances transparency, reduces inefficiencies, and improves security.
Blockchain’s Impact on the Banking Sector and the Future of Finance:
Blockchain is reshaping the banking sector by providing increased security, transparency, and cost savings. It is likely to play a pivotal role in the future of finance, ensuring the stability and trustworthiness of financial systems.
Smart Contracts: Transforming Efficiency in Banking: Smart contracts are transforming efficiency in banking by automating and self-executing predefined conditions, significantly improving the efficiency of transactions and reducing the need for intermediaries.
Reducing Fraud with Blockchain-Based Identity Verification in Finance: Blockchain-based identity verification in finance offers a secure and tamper-proof method of verifying customer identities, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft.
Blockchain’s Impact on International Payments and Cross-Border Transactions: Blockchain technology accelerates international payments and cross-border transactions by eliminating intermediaries and enabling real-time processing, potentially reducing costs.
DBS and the Blockchain Revolution in Banking: DBS actively participates in the blockchain revolution in banking by establishing blockchain-based businesses like DBS Digital Exchange (DDEx) and Partior, facilitating security tokens, digital currencies, and real-time payments.
The Evolving Role of Banks in the Age of Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
In the age of decentralized finance (DeFi), banks have an evolving role. While DeFi operates independently of regulatory frameworks, banks play a crucial part in maintaining the stability and trustworthiness of financial systems.
Blockchain Innovation Changing the Landscape of Financial Institutions: Blockchain innovation is changing the landscape of financial institutions by introducing new technologies and applications, potentially leading to increased security, efficiency, and transparency in the financial sector.
Blockchain’s Promise for Secure and Transparent Real Estate Transactions: Blockchain promises secure and transparent real estate transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring the trustworthiness of property transactions.
Empowering Energy Trading through Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology empowers energy trading by creating secure and transparent peer-to-peer trading systems, allowing individuals and organizations to buy and sell energy directly while efficiently monitoring transactions.
Read also about emerging banking technology:
:Embrace the Latest Innovations in Banking Technology for a Bright 2023
RBI’s article on Distributed Ledger Technology, Blockchain and Central Banks.